Data Analytics (Big Data)
Data Analytics is the science of examining raw data with the purpose of finding patterns and drawing conclusions about that information by applying an algorithmic or mechanical process to derive insights. The work of a data analyst lies in inference, which is the process of deriving conclusions that are solely based on what the researcher already knows; for example, running through a number of datasets to look for meaningful correlations between each other. Data Analytics is used in a number of industries to enable organizations to make better decisions as well as verify and disprove existing theories or models. Ecolab expert in the process of examining industrial data sets in order to enable organizations to make more-informed business decisions, increasingly with the aid of specialized systems and software.
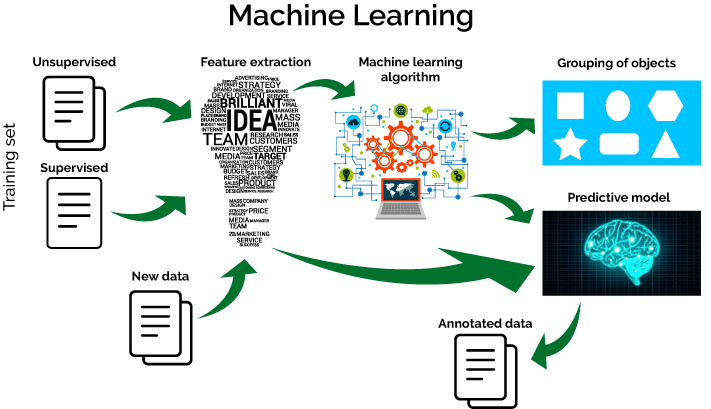
Machine Learning (Deep Learning)
Machine learning is the science of getting computers to act without being explicitly programmed. In the past decade, machine learning has given us self-driving cars, practical speech recognition, effective web search, and a vastly improved understanding of the human genome. Machine learning is so pervasive today that you probably use it dozens of times a day without knowing it. Many researchers also think it is the best way to make progress towards human-level AI.
Operations Research (OR)
OR encompasses a wide range of problem-solving techniques and methods applied in the pursuit of improved decision-making and efficiency, such as simulation, mathematical optimization, queueing theory and other stochastic-process models, Markov decision processes, econometric methods, data envelopment analysis, neural networks, expert systems, decision analysis, and the analytic hierarchy process. Ecolab is working on many research problems related to the OR. The followings are the most famous problems we concern about.
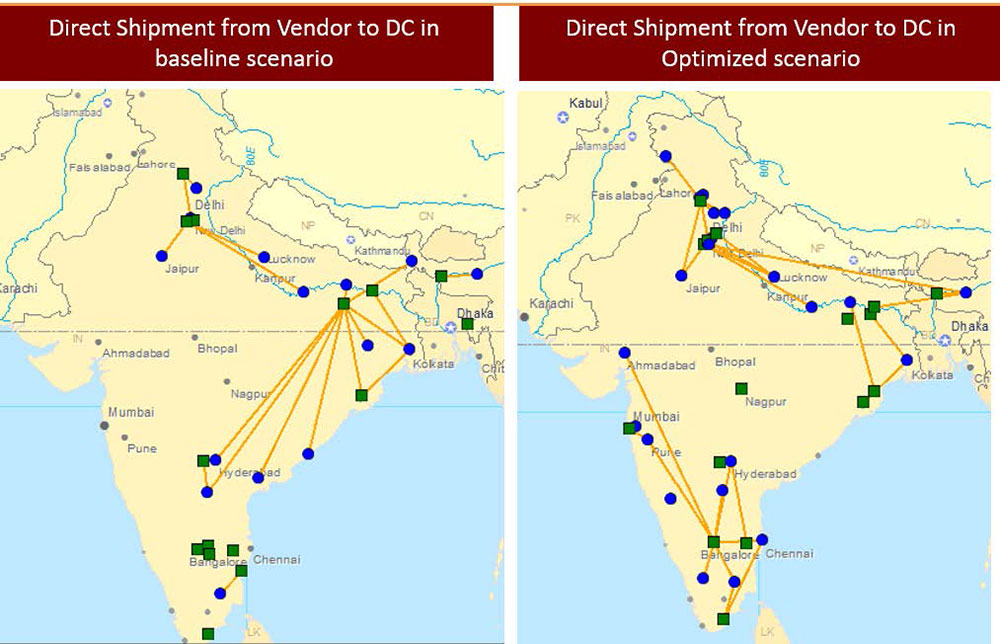
- Logistics is generally the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. In a general business sense, logistics is the management of the flow of things between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet requirements of customers or corporations. The resources managed in logistics can include physical items such as food, materials, animals, equipment, and liquids; as well as abstract items, such as time and information. The logistics of physical items usually involves the integration of information flow, material handling, production, packaging, inventory, transportation, warehousing, and often security.
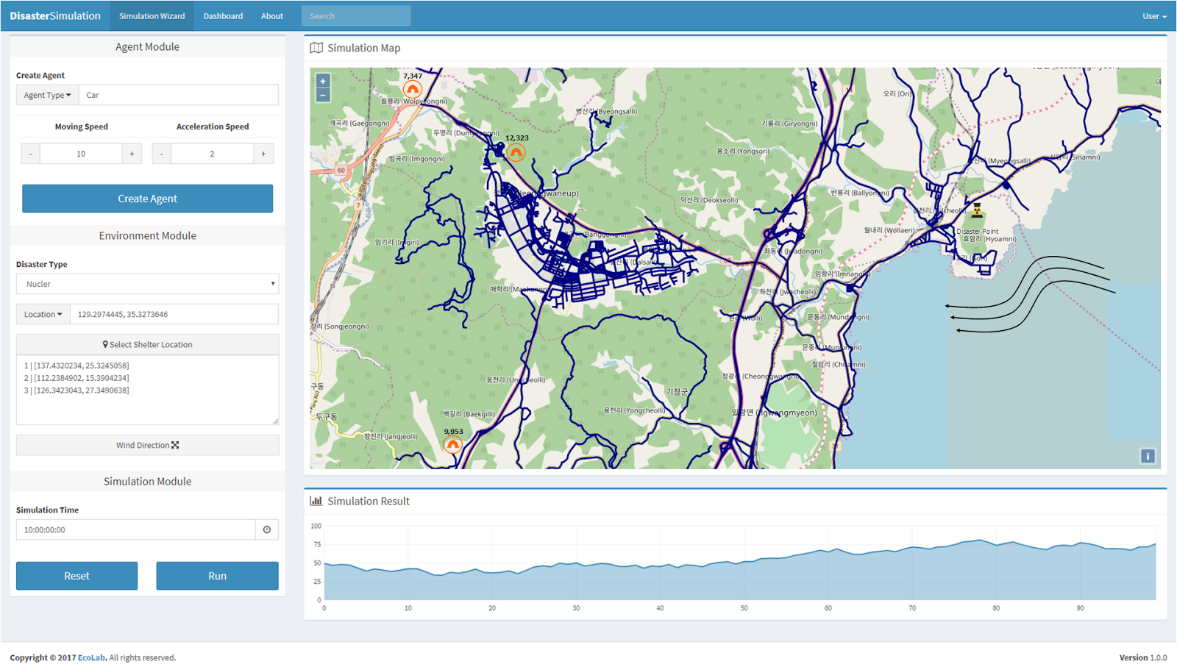
Modeling and Simulation
Simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time to investigate a wide variety of "What-if" questions about the real-world system. This method could be implemented in many cases such as traffic in transportation system and disaster event.
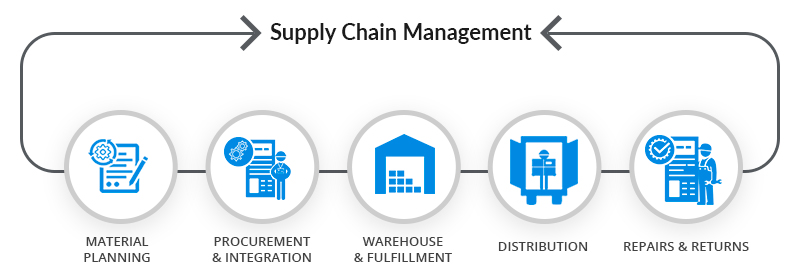
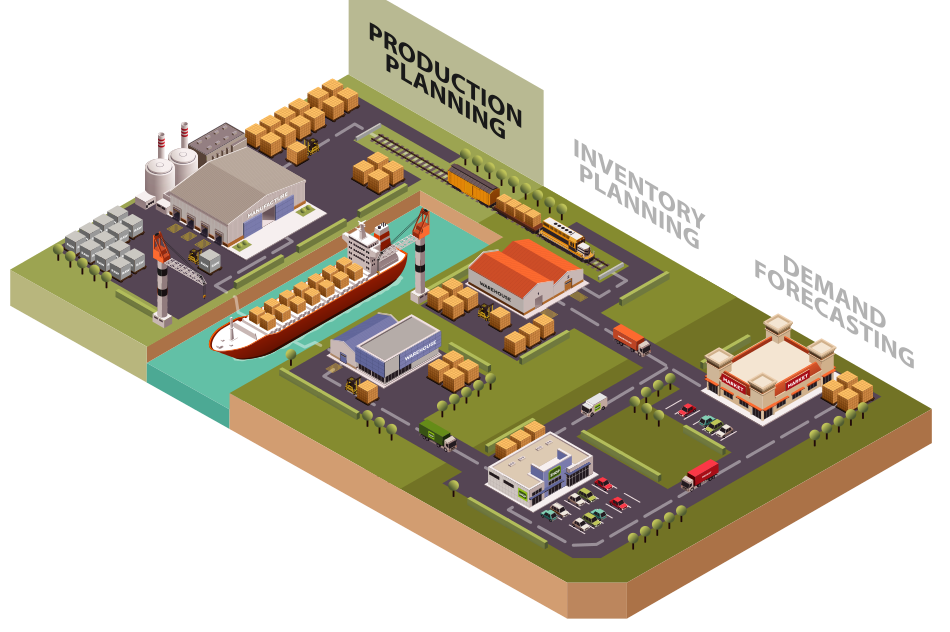
Supply Chain Management & Inventory
Supply chain management (SCM) is the active management of supply chain activities to maximize customer value and achieve a sustainable competitive advantage. It represents a conscious effort by the supply chain firms to develop and run supply chains in the most effective & efficient ways possible. Supply chain activities cover everything from product development, sourcing, production, and logistics, as well as the information systems needed to coordinate these activities. A component of supply chain management, inventory management supervises the flow of goods from manufacturers to warehouses and from these facilities to point of sale. A key function of inventory management is to keep a detailed record of each new or returned product as it enters or leaves a warehouse or point of sale.
Production Planning & Control
Production planning and control is the coordination of a series of functions according to a plan which will economically utilize the plant facilities and regulate the orderly movement of goods through the entire manufacturing cycle, from the procurement of all materials to the shipping of finished goods at a predetermined rate. It is a predetermined process which includes the use of human resource, raw materials, machines etc. PPC is the technique to plan each and every step in a long series of separate operation. It helps to take the right decision at the right time and at the right place to achieve maximum efficiency.
Computational Optimization
Computational Optimization and Applications covers a wide range of topics in optimization, including: large scale optimization, unconstrained optimization, constrained optimization, nondifferentiable optimization, combinatorial optimization, stochastic optimization, multiobjective optimization, and network optimization. It also covers linear programming, complexity theory, automatic differentiation, approximations and error analysis, parametric programming and sensitivity analysis, management science, and more. Computational optimization is an important paradigm itself with a wide range of applications. In almost all applications in engineering and industry, we almost always try to optimize something - whether to minimize the cost and energy consumption, or to maximize the profit, output, performance and efficiency. In reality, resources, time and money are always limited; consequently, optimization is far more important.
Manufacturing Process
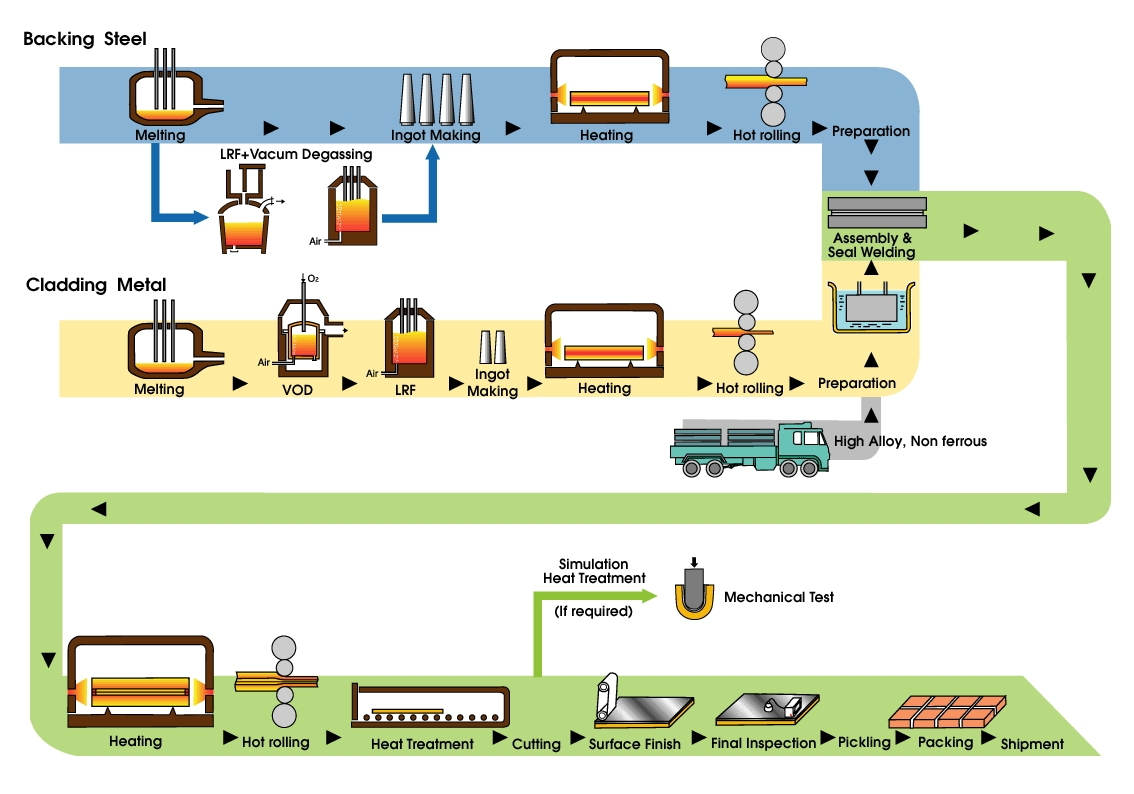
Manufacturing is the production of merchandise for use or sale using labour and machines, tools, chemical and biological processing, or formulation. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale. Such finished goods may be sold to other manufacturers for the production of other, more complex products, such as aircraft, household appliances, furniture, sports equipment or automobiles, or sold to wholesalers, who in turn sell them to retailers, who then sell them to end users and consumers. Manufacturing engineering or manufacturing process are the steps through which raw materials are transformed into a final product. The manufacturing process begins with the product design, and materials specification from which the product is made. These materials are then modified through manufacturing processes to become the required part. Modern manufacturing includes all intermediate processes required in the production and integration of a product's components. Some industries, such as semiconductor and steel manufacturers use the term fabrication instead.
Powder Injection Moulding
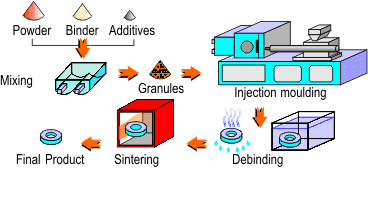
The powder injection moulding (PIM) process is an efficient method for the high volume production of shaped components from powders. PIM is a derivative of polymer injection moulding and uses much of the same technology, along with batch sintering processes used in powder metallurgy and ceramic processing. In PIM, polymeric binders are pre-mixed with metal or ceramic powders. The mixture is heated in a screw-fed barrel and forced under pressure into a die cavity, where it cools and is subsequently ejected. The polymer is then removed and the component sintered to the required density.
3-D Printing
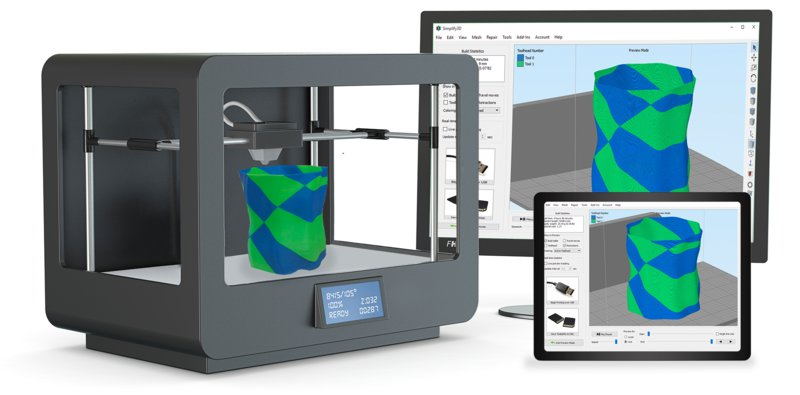
3D printing or additive manufacturing is a process of making three dimensional solid objects from a digital file. The creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive processes. In an additive process an object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the object is created. Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced horizontal cross-section of the eventual object. 3D printing is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing which is cutting out / hollowing out a piece of metal or plastic with for instance a milling machine. 3D printing enable to produce complex (functional) shapes using less material than traditional manufacturing methods.